Understanding WiFi: Common Problems and Solutions
As both an Internet Service Provider and business IT provider, LMi contends with a large number of issues related to WiFi on a daily basis. The symptoms of reported issues can vary greatly but the vast majority of these issues can be traced back to a few key concepts with regard to this ubiquitous technology. Given our expertise in this matter, we felt that it would benefit not only our members, but any party that’s experiencing issues with their internet, if we were to explain basic WiFi functionality, provide a non-exhaustive list of common WiFi problems, as well as some potential solutions. If you’re one of our members and have questions on the information below, or are experiencing an issue that you don’t feel is covered here, please don’t hesitate to contact us.
Starting with the basics, WiFi is a wireless radio broadcast used to connect your WiFi capable devices in or around your home or business to the internet. WiFi, on its own, does not provide internet and requires an internet connection (which doesn’t necessarily come with WiFi.) There are an innumerable number of WiFi transmitters ranging from your standard routers to advanced mesh systems from any number of manufacturers that we won’t be able to cover. Instead, we’ll focus on the general concepts by relating them to a simple analogy and introducing concepts, problems, solutions within the framework of that analogy.
The most common problems that our members report to us are related to buffering during video streaming, slow loading web pages, when web pages fail to load altogether, and not seeing or not being able to connect to your WiFi network. These issues typically stem from a few common factors or a combination of these factors. We’ll address each of the factors below and then offer some solutions, relating them back to the issues at hand.

As WiFI is a means to transmit information to, and from, your smartphone, computer, or other device to the internet, it’s similar in many ways to a discussion between two people, both in how loud each person can speak and how well they can hear the other person. If you’re standing right next to one another, then it should be simple enough to carry a conversation, but if you’re trying to speak to one another from across your home and through walls, it will be significantly more difficult. Your voice will get lost as it bounces off of walls and will be significantly reduced in volume when passing through walls. The same can be said for WiFi signals. Walls alone can account for a tremendous loss in signal strength, or how well your devices can hear and speak to one another. The thicker the walls, the harder it will be to carry a conversation through, or similarly, to watch video or browse the internet through. Additionally, multiple sets of walls (or ceilings and floors) will heavily impact the maximum range of your WiFi signal. Imagine yelling across your home or business to relay information, there will be a point where your voice will no longer be discernible, especially when we consider the other common factors below.


The second common factor, especially in high density areas such as apartments, is congestion. Congestion refers to the number of signals in your area and the amount that they interfere with one another. Moving back to the scope of a conversation between two people, congestion is the difference between talking in an empty room or in a crowded room. The more WiFi networks in your area, which you may see when you search for WiFi networks on your devices, the more likely you are to experience the effects of congestion. In addition to the number of signals in your area, the level of activity on those signals, and the WiFi channel that they occur on also come into play. WiFi can broadcast on a variety of channels, and changing channels can sometimes help prevent congestion. If you’re in the corner of a room carrying on a conversation, while there are other conversations going on in other corners of the room, there won’t be much of an issue with your own conversation (or the others with their own conversations). However, if the room is so crowded that discussions are happening directly to your left and right, it will become increasingly difficult to listen to and talk to one another. That, is congestion in a nutshell.
To a limited degree, your router or WiFi antennae will know to seek out less crowded channels but at a certain point, it will not be feasible to avoid congestion (at least to some degree). The final aspect of this issue is the increase in congestion when performing high bandwidth activities (teleconferencing, video streaming, downloads, uploads). This is simple enough to imagine, if you’re thinking of the data you’re using as a conversation. Greater internet usage is equivalent to more words spoken at a constant rate. It can be difficult to ask or answer a simple question when, to your right and left, are two excited conversations without pause. And it would be even harder to listen to someone tell you their story while others are telling their own stories near you. As such, high bandwidth activities are more likely to be impacted by congestion and also cause more congestion for others in your area.

Finally, the last common factor we’d like to cover is speed. This typically isn’t limited as much by WiFi as it is by your internet plan (or what’s available in your area), but it’s something that we’d like to cover due to the frequency of this issue. To start, your internet connection has a maximum potential of what it’s capable of sending and receiving. Sending would be information that you provide to the internet, such as uploading photos or the most common (and often forgotten), requesting information to be sent to you (such as opening a webpage, starting a video, etc.) Receiving is when information is provided to you, like when you’re looking at a picture or watching a video. It’s absolutely critical to understand that WiFi cannot provide unlimited speeds, there’s a limit to the amount of information that it can send and receive as well. We’re going to modify the analogy of a conversation to stress the importance of this distinction. Your internet speed is not the same thing as your internet speed over WiFi. For those with faster connections, running a speed test or using the internet while wired physically via ethernet will always be faster and more responsive than over WiFi.
As before, if WiFi is equivalent to the speed and clarity of a conversation between two people, then internet speed would be how quickly the person could comprehend and reply to said conversation. Slower internet speeds would be like explaining a complex topic to someone entirely new to it while faster speeds would be like a conversation between two experts in the same field. Again, we’d like to stress the difference between WiFi and internet speed. WiFi is like your ability to speak while internet speed is the thoughts before they are translated into speech. You can only speak as fast as you think, and you can’t comprehensibly speak faster than you think. In other words, your WiFi can’t be as fast or faster than your internet speed, and your internet speed will always be faster when wired directly than over WiFi.
Before delving into the various solutions that exist for the issues above, there’s another factor that can be problematic that is caused by the issues above. This is latency, which is essentially how long it takes for information to get from you to the internet or vice versa. Revisiting the previous factors, we’ll quickly go over how each can lead to latency. Firstly, with regard to WiFi range, your voice carrying over a long distance will echo and reverberate. It’ll be less clear and mix with ambient noise as well. The lack of clarity will mean that your voice and what you’re saying will be harder to comprehend and will sometimes need to be repeated. The same is true for WiFi signals. Devices at the far end of the usable range of the signal will often need to receive the same information multiple times due to the lack of clarity or not being able to hear the message altogether. In terms of congestion, or when there are a lot of signals (conversations) happening in your area, it can lead to messages needing to be repeated or pauses to ensure that the message has been understood. The same is true for WiFi where retries in congested areas can lead to delays in your internet experience which can mean longer load times or buffering. Finally, a lack of internet speed can lead to latency in that if too much information is being sent at one time, it can overwhelm the connection and cause information to not be processed (dropped packets.) This would be the same as instructions being read off to you at a lightning pace, faster than you can comprehend. As the list of instructions continue, it’s likely that you’d need to ask to go back to previous steps and would not be able to process all of the steps as they were read off, delaying the telling of a set of instructions.
The above list of issues is not exhaustive and our solutions below will, similarly, not be exhaustive. These are simply the most common issues and factors that we’ve experienced with our members. With respect to the above, these issues aren’t always immediately able to be diagnosed and don’t exist in a vacuum. Sometimes the issues are intermittent, only occurring at specific times such as peak hours when more people are streaming content and these issues often occur in conjunction with one another, complicating any diagnostic. Nonetheless, we have a few solutions to present for the above that have proven to be helpful in our experience.
If you’re running into issues with your connection (buffering, unresponsive, slow loading, etc.) then the first step is to run a speed test. This speed test should be done as close to your router or WiFi access point as possible and should be done with as few devices on the network as possible. This means that you should do it when no one is streaming, downloading files, or uploading data from your connection.
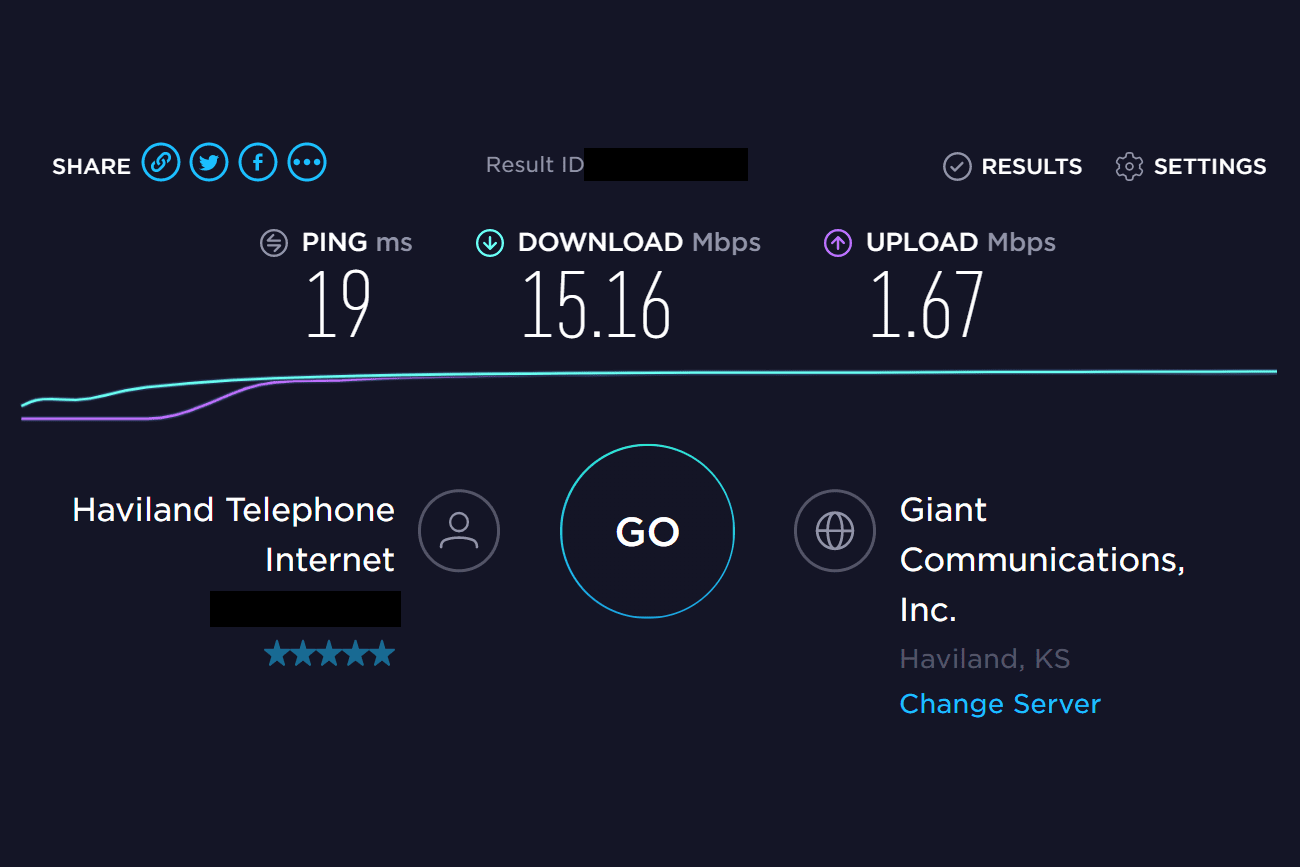
For reference, streaming content, on average, uses 6Mbps of your download bandwidth. If you’re seeing speeds below that, you’ll likely experience a loss in quality and likely some buffering as well. If you believe your speed to be an issue, contact us so we can see what options may be available in your area to improve your speeds. If we aren’t able to provide a more suitable service for your needs, we may still be able to advise on what other options would be the best fit for you. If your speed test performs well, then we’ll move on to other considerations.

The next step in narrowing down your issue to find a potential solution will require some consideration as to the nature of your issue. The common factors listed above can all lead to similar symptoms such as not being able to find your WiFi network, being unable to join your WiFi network, the inability to load web pages or videos, buffering when streaming content, or just general slowness while using the internet. In rare cases, it can be the fault of the streaming service or web page itself, so you should always test from multiple internet connections (such as your phone data) to verify your issue. Furthermore, if these issues aren’t always present, it’s very important to consider as it will make certain factors more probable than others.
There are a number of potential outcomes after we’ve verified that speed itself is not an issue and we’ll cover the common ones below. If you feel that we haven’t covered your particular circumstance, please contact us so that we can look further into your particular issue.
- If you’re testing at good speeds near your router but aren’t able to connect to your WiFi network or can’t see it from a particular area in your location, it’s most likely a range related issue.
- If you’ve tested good speeds but have issues that correspond to certain times of the day, you are most likely experiencing WiFi Congestion.
- If your speed test while next to your router are slower than expected, please contact us so that we can determine if there’s a better service option for you. Our newer service options can provide hundreds of times as much bandwidth at the same cost or with a marginal price increase, but are, sadly, not available in all locations currently.
As explained before, these issues are often not mutually exclusive and are more likely to be a compound issue. As such, it’s best to review what we consider to be the best practices for resolving WiFi related issues rather than delving into every possible combination of these issues. We’ll provide context to each step so that our readers can best determine which steps may be most suitable for them. If you’re an LMi member with one of our managed routers or WiFi networks, contact us so that we can assist with configuration changes at no charge. If you have your own router, you will need to login to your router and determine which of the following options are available and which, if any, are suitable for your situation. If you need help with that, you should check the physical unit itself as it will often provide directions on accessing its configuration page, or reach out to the manufacturer. If you’re relatively tech savvy, you may find the relevant information at https://setuprouter.com.
Best Practices for WiFi
- Most routers will allow for you to change the WiFi channel of your connection. Depending on your area, some channels will be more heavily used than others, making them more congested. Some devices will also allow for scanning of the environment to determine which channels are most appropriate for use in your area. Most modern routers will do this automatically, but it may not be doing it frequently enough or failing to assess the environment properly. There are a number of caveats that come with selecting WiFi channels that could effectively fill another blogpost but we’ll provide a general guideline.
- 2.4Ghz networks: There are 11 channels, adjacent channels will interfere with one another. Pick the channel that has the fewest networks on it with consideration to the adjacent numbers.
- 5Ghz: Pick the channel with the fewest networks
- As a caveat, you can also select the band of the radio (2.4 or 5Ghz). Wider bands both cause more congestion and are more susceptible to congestion but can provide higher speeds. If you are having issues related to congestion, you should select the lowest possible band (20vht for 2.4Ghz and 40vht for 5.0Ghz, typically).
- If your router is located in a corner of your house and you experience dead zones in the opposite corner, or if your router is located in another less central position, the best solution may be to try and move it to a more centralized position. Of course, this isn’t always feasible and it will depend on the nature of your connection and location. A good first step, if you have the router in a closed location such as a closet, cabinet, or underneath a desk, would be to elevate the device and ensure that it isn’t enclosed in a space. Beyond that, LMi offers wiring services that may be helpful in relocating your router.
- A more advanced option that we recommend (for more knowledgeable users), in cases where there isn’t enough internet speed available for one or more devices is Quality of Service. This is available on LMi’s current managed devices as we’ve tested its implementation on our devices but the same may not be true for our older, legacy devices or devices that we haven’t provided. If you’d like us to turn this on for LMi equipment at your home or business, contact us. Otherwise, it’s possible you may be able to find and configure the setting on your own equipment but we are unsure if it will make a noticeable impact or if it could potentially have a negative impact in your situation.
Hardware Solutions
There are also solutions that involve additional hardware. We’ll briefly discuss those third party solutions as well as include our own fully fledged WiFi solution for comparison.
- WiFi Extenders:
These are devices that connect to your existing WiFi network and then rebroadcast it. They aren’t typically supported by the router itself so configuring and troubleshooting the device can be more finnicky but if you’d simply like to extend coverage to one particular area in your home, it may be a suitable solution.
- High End Routers:
There are a large number of WiFi router manufacturers, each with their own product lines, so covering them all would be impossible. In the general case, more expensive routers will provide a greater range, more features, and more antennae to broadcast from to facilitate higher speeds and greater range. If you’re currently using an inexpensive router and feel that the signal is inconsistent (but still available) at the areas of your home furthest from your router, this may be a suitable solution.
- Mesh WiFi Products
These products have exploded in popularity in the past few years with major manufacturers each bringing their own iterations to market. These products provide a “main” device which serves as your router and extends the WiFi coverage by establishing dedicated links to other access points. They can range in price depending on available features and setup is typically driven by a phone app. Generally speaking, this is a great solution that can expand to cover even a large home with complete coverage as long as you’re comfortable with a more involved set up process.
- Always On WiFi from LMi
LMi offers our own mesh WiFi solution. While we don’t manufacture the Ubiquiti hardware that we use, we provide a complete solution that includes professional installation, monitoring, and is backed by our local customer support staff and dispatch team. The devices connect to one another via dedicated links to ensure stability and reduce potential issues. Our professional installers will be able to mount the equipment to further expand the range and can evaluate your specific situation to provide a comprehensive WiFi solution. For more information on that service, click here.
